26 June 2017
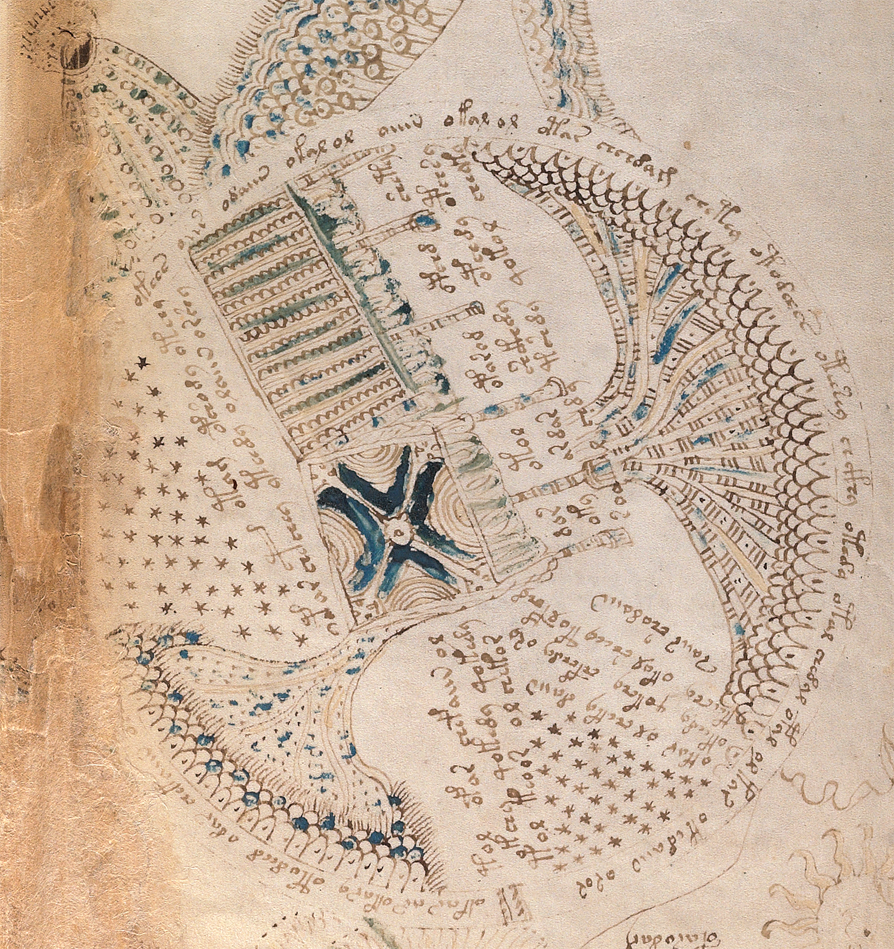
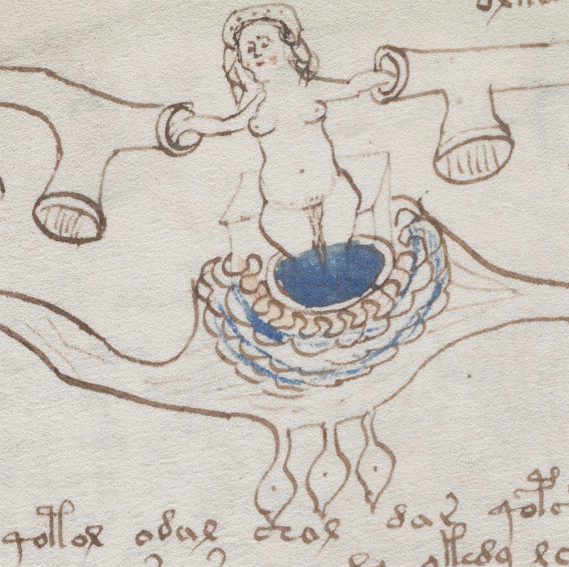
 On December 14, 2016, Searcher, on the Voynich.ninja forum, suggested that the cross-shaped item in the hand of a nymph on folio 79v might be a cross-staff. This was an intriguing idea, especially considering the way in which the instrument is held and the fact that there is another nymph holding something that looks like calipers, so I looked up some of the history of cross-staffs to see if there might be support for the idea.
On December 14, 2016, Searcher, on the Voynich.ninja forum, suggested that the cross-shaped item in the hand of a nymph on folio 79v might be a cross-staff. This was an intriguing idea, especially considering the way in which the instrument is held and the fact that there is another nymph holding something that looks like calipers, so I looked up some of the history of cross-staffs to see if there might be support for the idea.
The cross-staff is an ancient instrument which may trace back as far as the Chaldeans, who are also connected to early forms of astrology. In the Renaissance, it was used in navigation, but its original purpose was to study and measure distances related to the sun and stars. The staff provided a way to guide the eye and was the forerunner to instruments such as the quadrant and sextant.
Basics
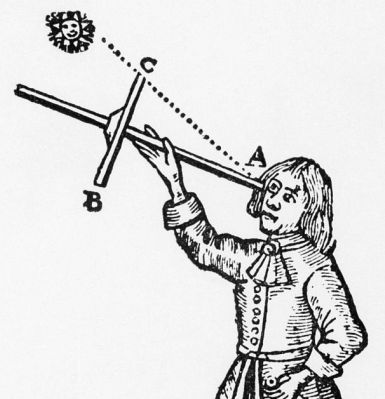 In its simplest form, the cross-staff consists of a rod with a smaller crossbar mounted at 90 degrees to the longer bar. The smaller bar is known as a “vane” or “transom”.
In its simplest form, the cross-staff consists of a rod with a smaller crossbar mounted at 90 degrees to the longer bar. The smaller bar is known as a “vane” or “transom”.
A cross-staff was held to the eye so the person using it could site along a line to the sun and compare this with the distance to the horizon. The vane was adjusted back and forth until both could be brought into view at the same time. Refinements included various means to move the crossbar, and markings on the instrument, in degrees and minutes, to help determine distance. Sometimes multiple vanes were added, but the basic instrument needed only one.
The cross-staff was sometimes known as Jacob’s staff. This may be based on the ladder Jacob envisioned stretching in a line from Earth to heaven. It has also been suggested that the name comes from one of the medieval names for the constellation we know as Orion, which has a short “belt” of stars resembling the vane on a cross-staff.
In French, it was called arbalete, rayon astronomique, and baton de Jacob, or arbalestrille for the marine version (the fore-staff). In Portguese, balestilha. In Latin, radius astronomicus, and in German, Jacobs-Stab or Stab und Kreuz, or just Kreuz.
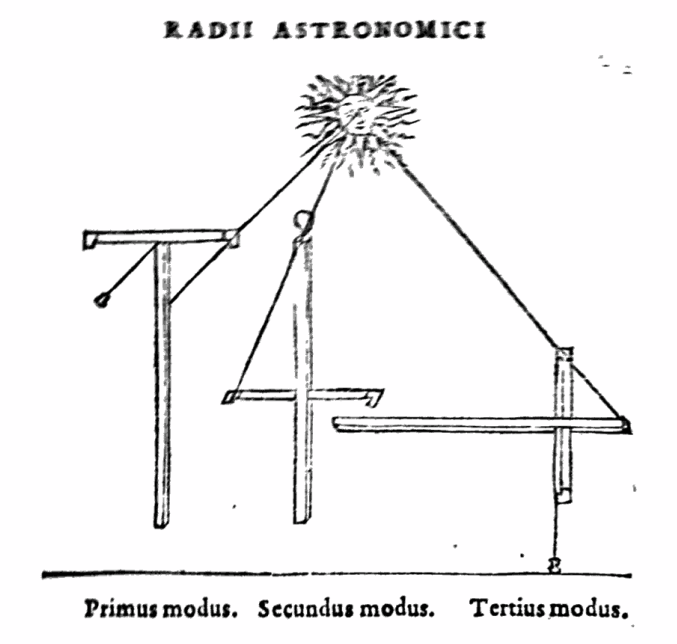
Three modes for using the cross-staff for siting and measuring are illustrated in Gemmae Frisii de radio astronomico et geometrico liber (Frisius, et al, Cavellat, 1557).
The earliest reference to the cross-staff, so far identified, is from 11th-century China. In Europe, the earliest references to modern use of the instrument are from Provençe in the 14th century. Of particular interest is a reference by Gersonides, a Jewish scholar who believed in astrology, who describes the instrument and attributes its uses not only to measuring distances between celestial bodies, but also their diameters.
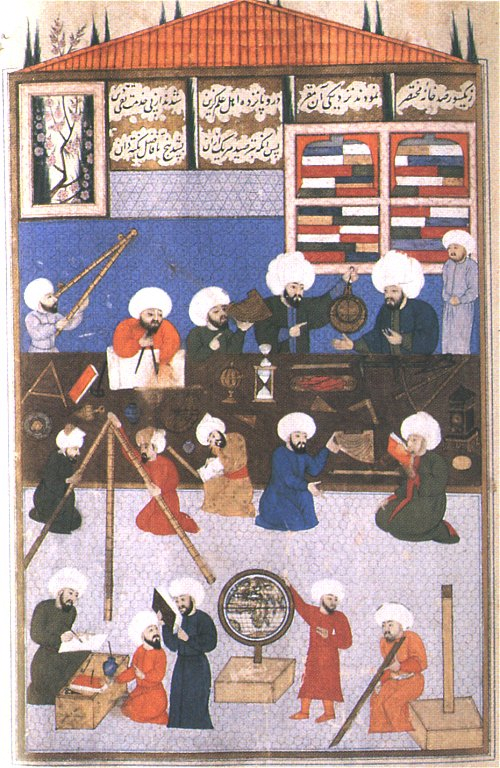

In this image, Moslem astronomers discuss the use of the astrolabe (upper right) and another uses a double sighting rod (left) while an early form of quadrant sits next to him on the table. The Q’uran (written in the 7th century) includes a passage about Allah/God having set out the stars to help navigation at night, thus inspiring an interest in the practical application of astronomy. [Image courtesy of the University of North Florida]
By the 19th century, a modified cross-staff with a round or square head, and sometimes a quadrant of slits, was used in surveying, in combination with a rod or chain and a number of staves. It was useful for measuring fields, platting lands, and certain forms of cartography.
The Cross-Staff for Navigation

Yemeni Astrolabe, 1291 [Courtesy of the Metropolitan Museum of Art: Edward C. Moore Collection]
f particular interest to Voynich researchers is the history of the cross-staff for navigation on water. In marine navigation, it was known as a fore-staff, so-called because the person using it faced the direction being observed, in contrast with the back-staff which was used with one’s back turned. Adjustments had to be made for how high the person was above the water.
It may seem surprising, but historians claim that the cross-staff was not used for marine navigation until fairly late in the middle ages.
In the Mariner’s Museum, they have this to say about the history of the cross-staff:
“…sailors did not use it until the early 1500s; the first recorded date was 1514. As with other early navigation instruments, the first use for the http://vintagegoodness.com/category/featured-collectibles/ Cross-Staff was in astrology, in measuring the altitude of stars to help forecast the future.”
William Wales notes, in 1744, that John Werner, of Nuremburg, recommended the use of the cross-staff as a marine instrument for determining longitude, by observing the distance between the moon and stars, in a book printed in 1514 (W. Wales, 1777), which is likely the same reference noted by the Mariner’s Museum.
In Motorboating (July, 1947), there is a practical description of the difficulties of using an instrument like a cross-staff on the sea:
“The pitching, rolling deck of a ship prevented general adaptation of the astrolabe. The cross-staff required the observer not only to sight directly on the blazing sun but also to look at two things simultaneously: the sun and the horizon. In the middle and high latitudes this latter job was not too difficult. In the low latitudes traversed by so many ships of the early days, it was nearly a physical impossibility to sight on a noon-day sun nearly overhead and a horizon dead ahead. These disadvantages led John Davis to invent, in 1590, his Back-Staff or Sea-Quadrant.”
Andrew MacKay, in 1793, sheds further light on why the cross-staff was not the instrument of choice for determining distance on water in the early days:
“The method of reckoning the latitude in degrees and minutes being introduced, instruments for observing altitudes were divided accordingly.– The Astrolabe, (a circular ring, having a moveable index and fights,) was applied to observe altitudes at sea. It was, however, supplanted by the Cross Staff, and that again by the Quadrants of Davis and Hadley, in succession.”
Thus, he suggests that use of the astrolabe preceded the cross-staff for marine purposes, with the quadrant eventually succeeding it.

On the left is a sighting rod (without crossbar), to the right, an astrolabe, constructed of overlapping, rotating rings—an instrument commonly used in navigation. Note the cloud band and the pattern in the background. [British Library, Bodley Digby 46, late 1300s]
Interpretation
If the object in the hand of the nymph on folio 79v is a cross-staff, then it’s unlikely that it’s intended as a marine navigation instrument—the astrolabe and other means were more commonly used for this purpose before the 16th century. In the early 15th century, the cross-staff was primarily used for land navigation, architectural measurement, and astrology.
 Unfortunately, the other images on the page, below the cross-wielding nymph, add little to our understanding of the cross-shaped object unless, perhaps, the Jacob’s Ladder story is being used in a metaphorical way and the presence of a nebuly-like “umbrella” over the nymph and her crow’s-next viewpoint are pointing to a path to heaven, a concept particularly prevalent in Christian iconography, but common to many cultures.
Unfortunately, the other images on the page, below the cross-wielding nymph, add little to our understanding of the cross-shaped object unless, perhaps, the Jacob’s Ladder story is being used in a metaphorical way and the presence of a nebuly-like “umbrella” over the nymph and her crow’s-next viewpoint are pointing to a path to heaven, a concept particularly prevalent in Christian iconography, but common to many cultures.
Or perhaps it’s the astrological significance of the cross-staff that is alluded to in the Voynich manuscript. If the various nymphs are personifications of constellations, as suggested by Koen Gheuens, it would not be out of place to find a cross-staff aimed at the stars or a possible connection with Jacob’s rod, which was traditionally associated with Orion’s belt.
J.K. Petersen
Copyright © 2017, All Rights Reserved

 Postscript April 21, 2018: I have added one more tunic to the map originally posted July 7, 2017.
Postscript April 21, 2018: I have added one more tunic to the map originally posted July 7, 2017.